We can use recursive class initialisation to define a linked list:
class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
}We can then create two constructors:
class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
// This means next is null as ListNode
}
public ListNode(int value, ListNode next) {
this(value); // Calls the other constructor ListNode(int)
this.next = next;
}
}We then have recursive initialisation:
ListNode last = new ListNode(30);
ListNode middle = new ListNode(20, last);
ListNode first = new ListNode(10, middle);
// Is equivalent to
ListNode first = new ListNode(10, new ListNode(20, new ListNode(30)));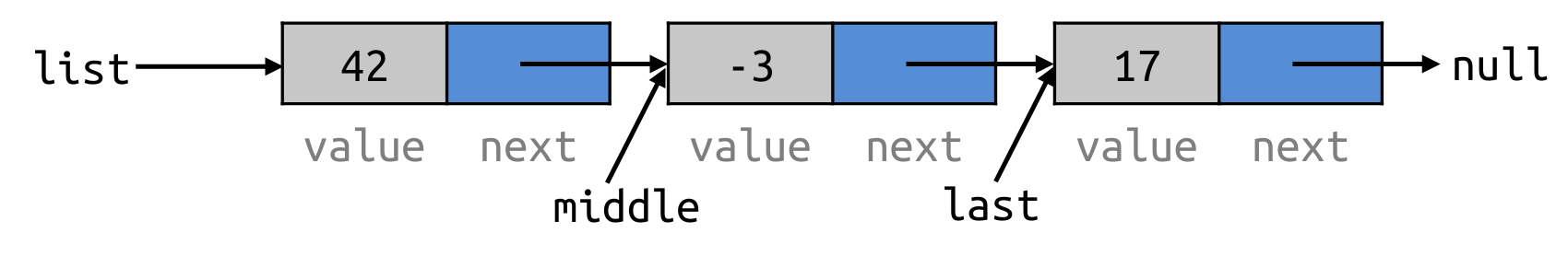
Operations on LL
We have LinkedList LL = ....
To insert at the beginning: list = new LinkedList(10, list); to insert 10 at the beginning.
To insert at the end: list.next.next...next = new ListNode(10); appends at the back.
Nested Classes
We can nest the class definitions to make the ListNode unavailable outside of the LinkedList implementation.
public class LinkedList {
private class ListNode {
private int value;
private ListNode next;
}
private ListNode front;
public LinkedList() {
front = null;
}
}We are not allowed to initialise an object of type ListNode in a static method of LinkedList!