Declaration and Initialisation
Every primitive variable in a local scope must be both declared and initialised before being used. Note that this is not true for instance level variables, like class attributes.
Once we have declared a variable for a scope, we cannot re-declare it.
Examples:
teeth = 28 // Error not declared!
int teeth = 1; // Valid
int teeth = 10; // Already declared error!
double teeth = 10.0; // Already declared error!Primitive Types
Double
A double can be initialised with both a 243.2342 value, but also with exponential notation 1e-2.
Note that a double can also be ++ incremented, just like an int.
Arithmetic evaluation in Java
Modulo
The modulo operator works as follows:
(a / b) * b + (a % b) = a where a / b is the integer division (with rest).
So -11 % 4 is equal to -3 and not 1.
In general, if the a is negative, the result is negative.
Associativity
+, *, /, % are left-associative, meaning that X op Y op Z = (X op Y) op Z.
= for example is right-associative. That is also why a = b = c = 5 means all are equal to 5.
Operator precedence
*, /, % binden stärker als +, -.
Unary operators (-) bind stronger than binary ones.
== and other comparison operators have higher precedence than the boolean comparison operators like &&.
Implicit ()
First operators with higher precedence are bound, ex: 2 * x + 3 = (2 * x) + 3.
Then if two operators have the same precedence, then associativity is relevant:
x - 7 + y→(x - 7) + ybecause of same precedence and left-associativex = y = 0→x = (y = 0)because of same precedence and right-associative
Typecasting
(type) expression is the cast-operator, which is unary (highest precedence) and right-associative.
It’s also higher-precedence than all other arithmetic operators.
Casting from lower-precision types (int → long, int → double) is always implicit. Down-casting into less bits has to be explicit.
The only special case is long → double, which is implicit, even though we may incur precision-loss.
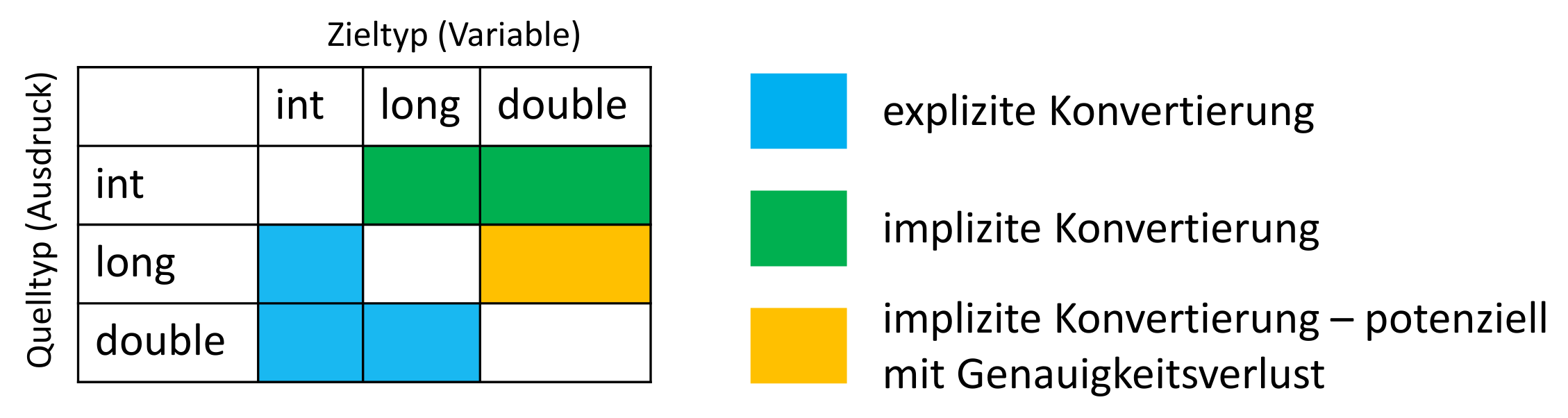 Keep in mind the explicit casts will be a compile error if the cast is not specified.
Keep in mind the explicit casts will be a compile error if the cast is not specified.
String Typecasting:
Doing + with a string will cast any primitive type to a string representation.
Errors
n % 0 and n / 0 both throw the divide by zero error.
Negative Number Gotchas
Dividing by a negative number gives a negative result: 10 / -2 = -5.
Modulo a % b can also return negative results:
- So
-11 % 4is equal to-3and not1. - In general, if the
ais negative, the result is negative.
Scanner
The Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in) (you can also use file handles as inputs, using new File("file.txt")) allows for the methods:
nextInt()to consume the nextintfrom the input.nextDouble()…next()reads a one-word string (delimited by spaces and newlines)nextLine()reads in the entire next line
Randoms
Use Random rand = new Random() to generate random numbers.
nextInt()returns the next random integer (range overint.MIN_VALUEtoMAX_VALUE)nextInt(n)random integer in the range[0, n).nextDouble()random real number in the range `[0.0, 1.0)